

Background and History
Development
In February 2004, a development team, composed of 16 educators was formed to create the Developmental Continuum for Literacy with ICT Across the Curriculum. These educators were Kindergarten to Grade 8 teachers, many of whom came from regional, French and Aboriginal milieus.
Inquiry
This team carried out the development of the continuum as an inquiry. In preparation, the team drafted essential questions and an inquiry plan. They also gathered secondary source data to determine how educational jurisdictions within Manitoba, in other provinces and internationally use ICT to support and extend learning. The team examined sample continuums representing literacy in reading, writing and numeracy. Based on the findings of these investigations, the members of the development team carried out action research in their schools and classrooms to gather primary source data to inform the development of the continuum. Their direct interactions with, and observations of, students have ensured that the continuum meets the needs of students in Manitoba.
Building the Descriptors
Teachers on the development team observed how students in their classrooms use ICT in their learning. In grade groupings, the team analyzed its observations and wrote descriptions of students’ behaviours. They viewed these descriptions through multiple lenses and filters, such as different curricular areas and multiple intelligences, to validate content, eliminate overlaps and identify gaps. Their analysis informed the next set of strategic classroom observations. This was a recursive process that refined and simplified the observations to articulate them into descriptions. These descriptions became the “descriptors” in the continuum.
Constructing the Continuum
As the teachers refined the descriptors that formed the building blocks of the continuum, they organized and reorganized, constructed and deconstructed, the framework of the continuum. Ultimately, the team represented the continuum as a two-dimensional matrix that presents the descriptors in three stages of thinking across an horizontal axis. They used the vertical axis to categorize the descriptors into nine Big Ideas: five in the Cognitive Domain and four in the Affective Domain of the continuum.
Which Models Informed the Creation of the Developmental Continuum for Literacy with ICT?
- Bloom’s cognitive taxonomy and Krathwhol’s affective taxonomy
- Inquiry (described variously in subject areas as scientific inquiry/ problem-solving/ managing information, et cetera)
- Pearson and Gallagher’s Model of Explicit Instruction, which portrays the gradual release of responsibility from teacher to student
Why Were These Models Used?
- Teachers have prior knowledge of, and experience with, the models and the taxonomies.
- Research in the last 20 years has shown that the most effective way to infuse ICT is to focus on pedagogy rather than on technology.
- The pedagogy of Literacy with ICT Across the Curriculum encourages movement from “ICT as supplementary to the curriculum” to a model that infuses ICT across the curriculum.
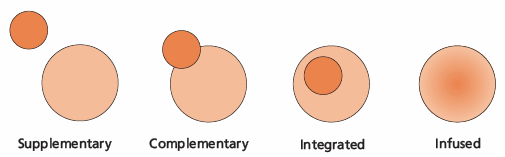
- A supplementary relationship separates ICT and curriculum in space, time, and personnel - separate computer labs, computer classes and computer teachers.
- A complementary relationship begins to connect ICT with curriculum in various ways.
- An integrated relationship allows the classroom teacher to bring ICT into the classroom so it is available at teachable moments.
- An infused relationship allows the transparent application of ICT, wherever and whenever appropriate, to enhance critical and creative thinking.