Grades 5 to 8 English Language Arts: A Foundation for Implementation
Implementation Overview: Grades 5 to 8
Literacy Learning Through the Six Language Arts -Part 2
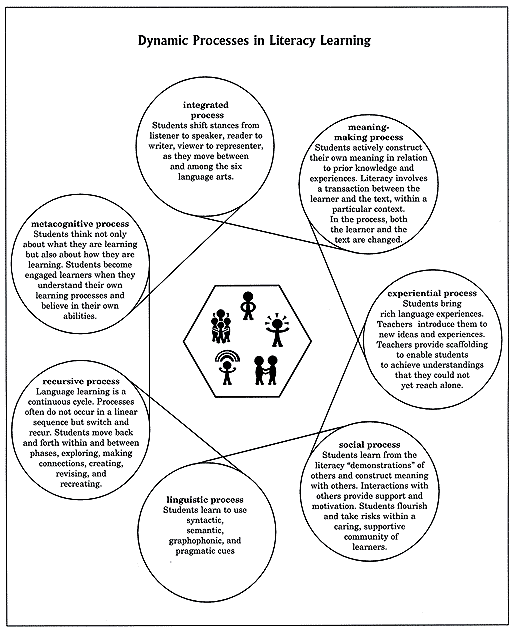
Dynamic Processes in Literacy Learning
Literacy learning involves many processes. The diagram entitled Dynamic Processes in Literacy Learning (see below) identifies some of the key processes that form the conceptual underpinnings for effective literacy learning in language arts classrooms.
Common Processes in the Six Language Arts
The six language arts share common learning and cognitive processes. Reading, viewing, and listening processes are concerned with constructing meaning from texts created by others. Writing, speaking, and representing processes are concerned with constructing meaning in order to communicate with others. In the construction of meaning, learners are involved with both the expressive and the aesthetic qualities of language, and also with its transactional purposes (the exchange of ideas and information).
The diagram entitled Common Processes for Making Meaning in the Language Arts illustrates the processes for effective literacy learning in a totally integrated language arts curriculum. The centre column of this diagram identifies the learning processes common to all six language arts. The left side of the diagram indicates how comprehension processes are used in constructing meaning from the texts of others; the right side indicates how composing processes are used in creating texts to learn and to communicate with others.
Literacy learning is always focussed on the integration of new information with the prior knowledge the student brings to the task. While the Before, During, and After framework can be superimposed onto this diagram, learning processes need to be seen in terms of a continuously recursive and renewing cycle of language learning and growth. Integration of information occurs within all literacy processes. Students become more proficient in the processes with effective teacher modelling, guided instruction, and practice. Over time, they learn to comprehend and compose increasingly more complex and sophisticated texts on their own.
Back to Implementation Overview: 5 to 8


